Global Wind Turbine Tower Market: Growth, Trends, and Future Outlook
 Tejask Kam
29 Aug, 2025
10 mins read
24
Tejask Kam
29 Aug, 2025
10 mins read
24
Introduction
Wind energy has emerged as one of the most reliable and sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels in the global energy mix. At the heart of this transformation are wind turbine towers, which act as the backbone of every wind energy installation. These towers support the nacelle and blades, elevating them to optimal heights where wind speeds are stronger and more consistent. As nations across the globe increase their focus on clean energy, the demand for advanced and taller wind turbine towers has seen exponential growth.
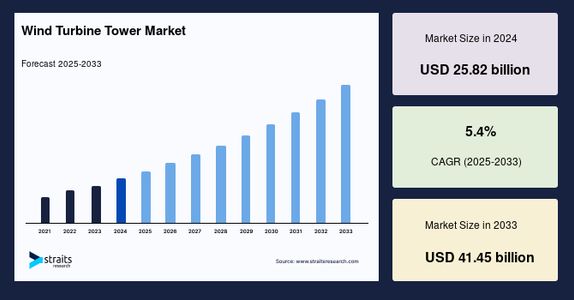
The global wind turbine tower market size was valued at USD 25.82 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 27.22 billion in 2025 to USD 41.45 billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.4% during the forecast period (2025-2033).
Market Dynamics
1. Key Growth Drivers
- Global Renewable Energy Push
- Governments and private stakeholders are aggressively pursuing decarbonization goals. Wind energy, particularly offshore wind, is being prioritized as a scalable, cost-efficient, and carbon-free source of power. This directly increases demand for turbine towers.
- Advancements in Tower Design
- The move toward taller towers allows turbines to access higher altitude winds, improving energy output. Hybrid materials such as steel-concrete combinations and the introduction of wooden towers are enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and flexibility.
- Expansion of Offshore Wind
- Offshore wind is emerging as a game-changer, especially in Europe, China, and the U.S. Offshore towers require greater structural integrity and innovative engineering solutions, opening opportunities for specialized manufacturers.
- Localized Manufacturing
- Transporting large tower sections across borders can be prohibitively expensive and logistically challenging. As a result, companies are establishing regional fabrication plants, which cuts costs, reduces emissions, and improves project timelines.
2. Market Challenges
- High Initial Costs
- Wind turbine towers involve significant investment in raw materials, manufacturing, and installation. Offshore towers, in particular, require advanced construction techniques and specialized vessels.
- Raw Material Volatility
- Steel, the primary material in tower production, is subject to price fluctuations, which can disrupt project budgets and timelines.
- Engineering & Maintenance Complexities
- Taller towers and offshore installations face technical issues like stability, transport challenges, and ongoing maintenance in harsh environments.
- Regulatory & Environmental Barriers
- While wind energy is environmentally beneficial, land-use conflicts, marine ecosystem concerns, and government permitting processes can delay projects.
Segmentation Analysis
By Installation
- Onshore Towers
- Onshore continues to dominate due to lower costs and simpler logistics. These towers remain central to the renewable strategies of countries like the U.S., India, and Brazil.
- Offshore Towers
- While offshore represents a smaller share, it is the fastest-growing segment. Rising investments in offshore wind parks in Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the U.S. are driving demand for corrosion-resistant, high-capacity towers.
By Material
- Steel Towers
- Still the most widely used due to durability and proven reliability.
- Concrete Towers
- Gaining ground, particularly in taller installations, as they avoid some transport challenges of steel towers.
- Hybrid Towers
- Offer the best of both worlds, combining the strength of steel with the adaptability of concrete.
- Wooden Towers
- A recent innovation, led by Scandinavian companies, that utilizes laminated wood as a sustainable, recyclable material.
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific
The largest market globally, driven by rapid deployment in China and India.
- China continues to lead in onshore installations and is now making significant offshore investments.
- India, supported by government incentives, is emerging as a major hub for wind energy projects.
Europe
A pioneer in offshore wind energy, with countries like Germany, Denmark, and the UK leading in offshore installations. Europe is also adopting wooden towers and investing in sustainable manufacturing.
North America
The U.S. is the primary growth engine, particularly in offshore projects along the East Coast. Policy incentives like the Inflation Reduction Act are accelerating renewable investments.
Latin America
Countries like Brazil and Mexico are increasing investments in onshore wind, supported by favorable wind conditions and renewable energy targets.
Middle East & Africa
Still in early stages but showing promise. South Africa is leading the region’s wind energy projects, while Gulf nations are exploring large-scale renewable adoption to diversify away from oil dependency.
Competitive Landscape
The global wind turbine tower market is highly competitive, with companies investing heavily in R&D, localized manufacturing, and partnerships. Key players include:
- Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy – A leading name in both onshore and offshore wind projects.
- Vestas Wind Systems – Known for innovative designs and global presence.
- CS Wind Corporation – Operates the world’s largest wind tower manufacturing facility.
- Arcosa Wind Towers – Expanding its U.S. operations with new factories.
- Modvion – Pioneer of wooden tower technology, offering sustainable alternatives.
- Marmen Inc. and GRI Renewable Industries – Important players in steel and hybrid towers.
- CNBM – A Chinese leader focusing on cost-effective solutions.
Strategic moves include mergers, acquisitions, and regional manufacturing expansions to cater to growing demand and reduce transport costs.
Technological Innovations and Trends
- Wooden Towers
- Wooden towers made from laminated veneer lumber are emerging as a lightweight, recyclable, and eco-friendly alternative to steel. They can be manufactured in modular parts, simplifying transportation and assembly.
- Digital Twin Technology
- Towers integrated with digital twin systems enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimization of operations.
- Spiral-Welded Towers
- A revolutionary manufacturing method that allows towers to be produced in modular spirals on-site, reducing transport issues and lowering costs.
- AI & Simulation
- Artificial intelligence is being used to simulate tower designs, optimizing weight, load-bearing capacity, and structural stability under different wind conditions.
- Floating Offshore Towers
- Essential for deepwater offshore wind farms, floating towers are gaining attention as a feasible solution for countries with limited shallow waters.
Market Outlook
The future of the wind turbine tower market looks robust, underpinned by a global shift toward clean energy. Offshore projects will be the strongest growth driver, while hybrid and wooden towers will add diversity to the materials mix. Governments and private players will continue to invest heavily, and localized manufacturing will become standard practice.
By 2033, wind turbine towers will not only be taller and stronger but also smarter, more sustainable, and digitally integrated. Innovations like floating platforms and AI-powered predictive monitoring will reshape the industry landscape, making towers more efficient and reliable.
Conclusion
The wind turbine tower market is a cornerstone of the renewable energy transition. From steel and concrete to hybrid and wooden designs, tower technology continues to evolve rapidly. With Asia-Pacific leading in scale, Europe advancing offshore innovations, and the U.S. accelerating renewable adoption, the market is poised for strong growth.
While challenges such as material costs, engineering complexity, and environmental concerns persist, the sector’s innovation pipeline is robust. By blending sustainability with advanced technology, the wind turbine tower industry is set to play a pivotal role in meeting global clean energy targets and reducing carbon footprints in the decades ahead.
Written By:
Tejask Kam



Hotels at your convenience
Now choose your stay according to your preference. From finding a place for your dream destination or a mere weekend getaway to business accommodations or brief stay, we have got you covered. Explore hotels as per your mood.